If you’ve been following my blog recently, you’ve probably heard about Microsoft Fabric. But what exactly is the Microsoft Fabric Data Warehouse? Does Microsoft Fabric even have a database? How do you create a data warehouse inside it? Don’t worry, because this post will answer all those questions in a simple way.
What Is Microsoft Fabric Warehouse?
At its core, Microsoft Fabric is Microsoft’s latest all-in-one analytics platform. Think of it as a tool that brings together everything you need to store, process, analyze, and visualize data – all under one roof. Whether you are a data engineer, data scientist or data analyst, you can use Microsoft Fabric to do your job. And yes, a big part of this platform is its Data Warehouse.
The Microsoft Fabric Data Warehouse is where your structured data lives. You might be wondering what is the difference between a lakehouse and data warehouse in Microsoft Fabric. The answer depends on the type of data you’re working with and what you want to achieve. In general, a data warehouse is best when you’re dealing with structured, relational data like sales records, customer information, or financial transactions. It’s designed for fast SQL queries, clear data structures, and reporting needs, making it ideal for building dashboards and business intelligence reports, especially when using tools like Power BI.
On the other hand, a lakehouse is more flexible and is better suited when your data comes in various formats. If you’re working with raw files like logs, JSON, images, or unstructured data, a lakehouse will serve you better. It allows you to store large volumes of raw data without enforcing strict schemas, making it perfect for data science, machine learning projects, or scenarios where your data structure might change over time.
In many cases, companies use both together: the lakehouse stores raw, unstructured data, while the data warehouse holds cleaned, structured data ready for reporting and analysis. Think of the lakehouse as your raw data storage area and the data warehouse as the place where your polished, report-ready data lives.
Does Microsoft Fabric Have a Database?
This is a question I hear often: Does Microsoft Fabric have a database?
The short answer is: yes, but a modern version of database.
While the data warehouse in Microsoft Fabric looks and feels like a traditional SQL database (you can create tables, define schemas, and write SQL queries against it), it’s actually built on a modern architecture.
Unlike a traditional SQL Server database, where everything is stored on a single server or cluster, Fabric’s warehouse is designed to scale automatically as your data grows, without you needing to manage servers or infrastructure.
In simple terms: Microsoft Fabric’s data warehouse behaves like a SQL database for the end user, but under the hood, it’s a cloud-based, distributed system optimized for big data analytics.
Instead of using traditional SQL Server databases like in the old days, Microsoft Fabric uses cloud-based technology powered by OneLake, Microsoft’s unified data lake storage. Inside Fabric, your data warehouse acts as a type of database – it stores structured, relational data, and you can query it using standard SQL language.
In other words, if you’re familiar with SQL databases, working with Fabric’s data warehouse will feel very similar, but behind the scenes, it’s optimized for cloud and big data workloads.
Microsoft Fabric Data Warehouse Data Types
Now, what about data types in the Fabric Data Warehouse?
Here’s the good news: if you’ve used SQL Server or similar databases, you’ll feel right at home. Microsoft Fabric supports standard SQL data types such as:
- INT (whole numbers)
- DECIMAL / NUMERIC (for precise numbers)
- FLOAT (for approximate numbers)
- VARCHAR / NVARCHAR (for text)
- DATE / DATETIME (for dates and timestamps)
- BOOLEAN (for true/false values)
These standard data types help keep things simple. Your existing SQL knowledge will apply, making it easy to structure your tables and store data just like you would in a typical relational database.
How to Create a Data Warehouse in Microsoft Fabric?
If you’re wondering how to create a data warehouse in Microsoft Fabric, don’t worry, because it’s not as complicated as it sounds. Here’s a simple step-by-step overview to get you started:
The first step is to go to the workspace where you want to create a data warehouse. What I usually do is to create a separate folder for warehouses:
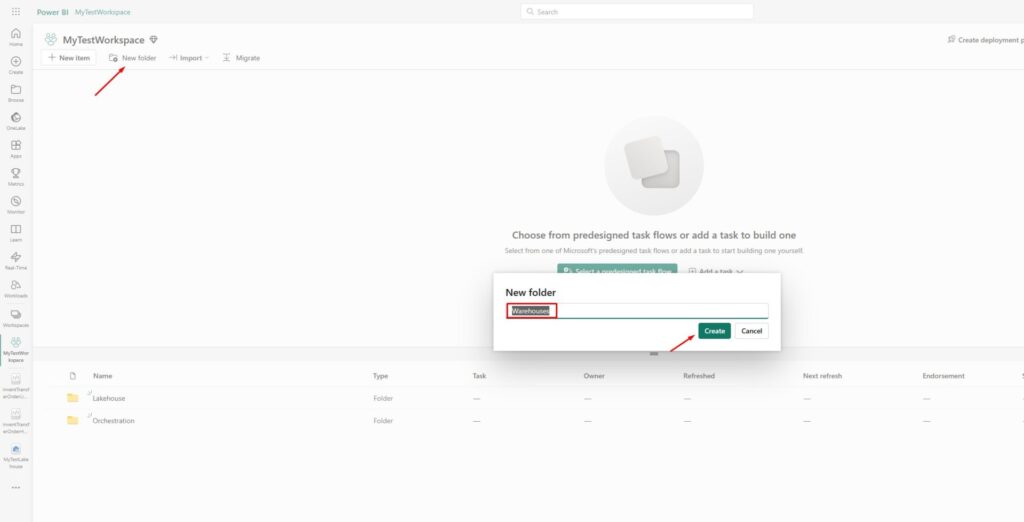
Next step is to create a data warehouse itself. Go to the Warehouses folder you just created, click on New item and find Warehouse option in All items section:
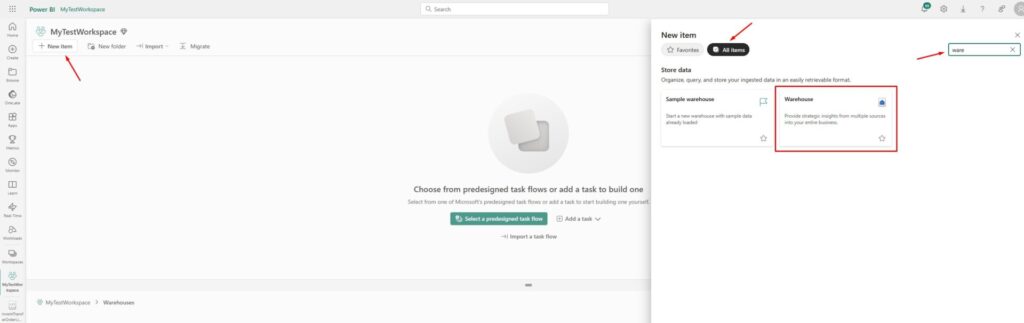
Choose the desired name for your data warehouse and click on Create:
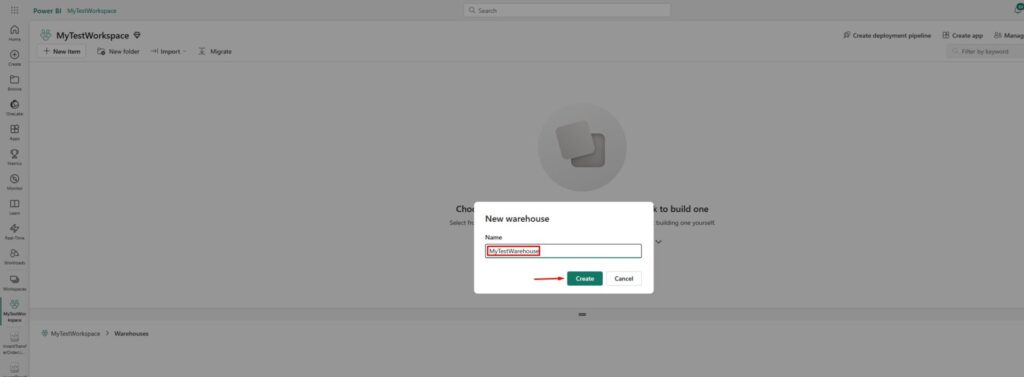
After a few moments, the data warehouse will get created, but you will see there are still no tables inside:
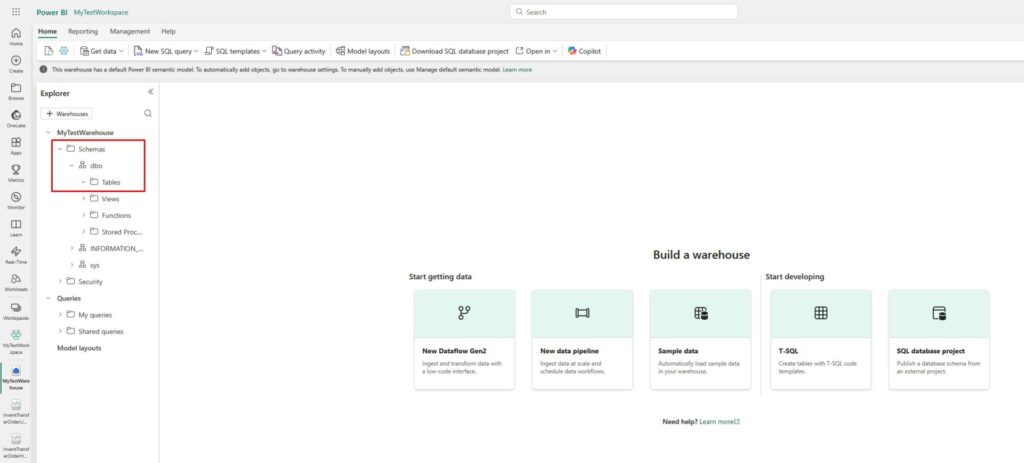
Let’s ingest some data to our data warehouse. If you already have a lakehouse where you prepared some structured data, this should be an easy task. First, create a separate folder where you will keep all the items you usually use for data orchestration (e.g. notebooks and pipelines):
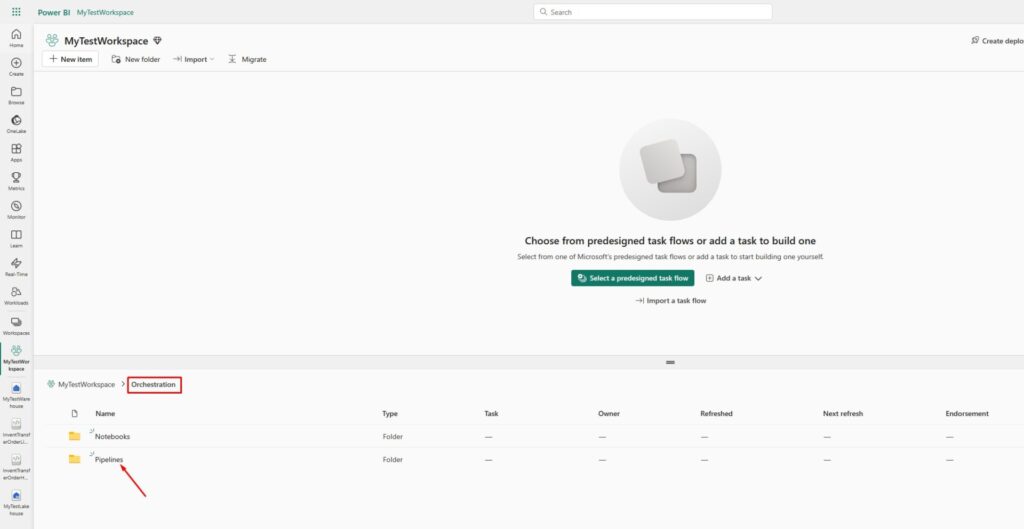
Go to the Pipelines folder and create the new pipeline:
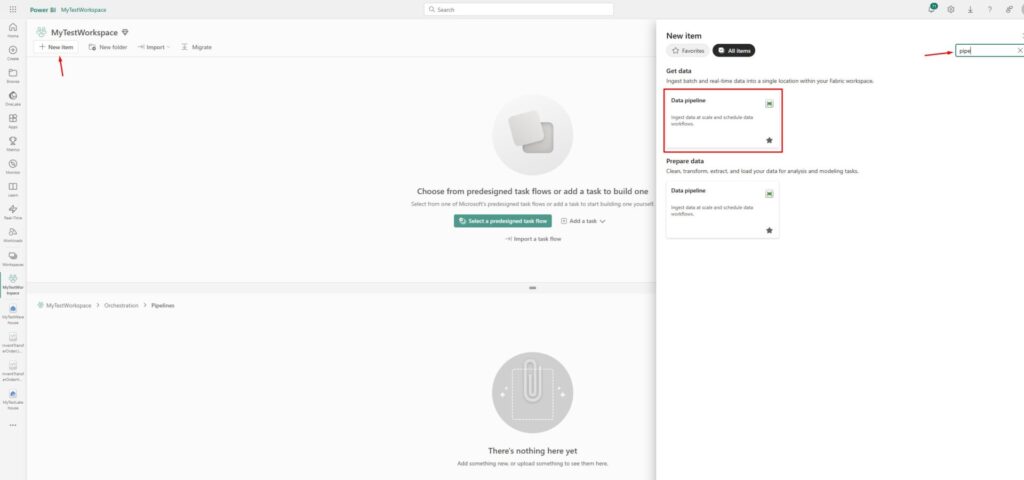
Now, we will use the Copy Assistant to copy the data from lakehouse to the data warehouse we just created:
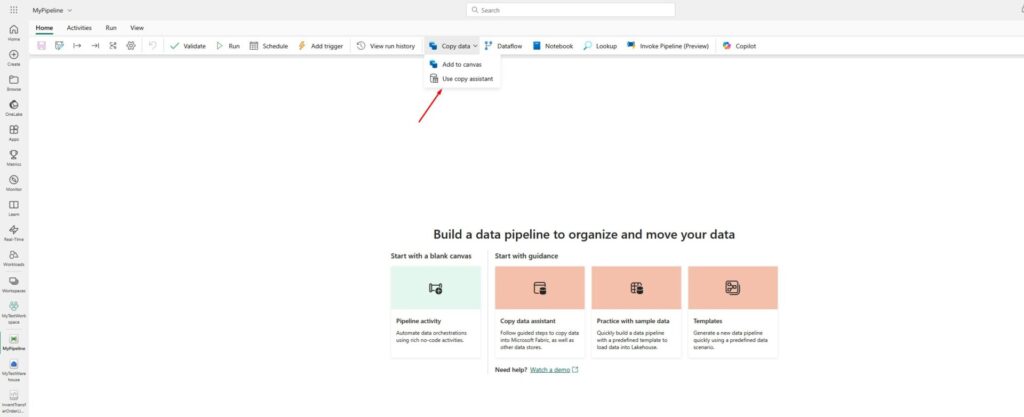
Let’s choose our lakehouse as a data source, and click Next in the bottom-right corner:
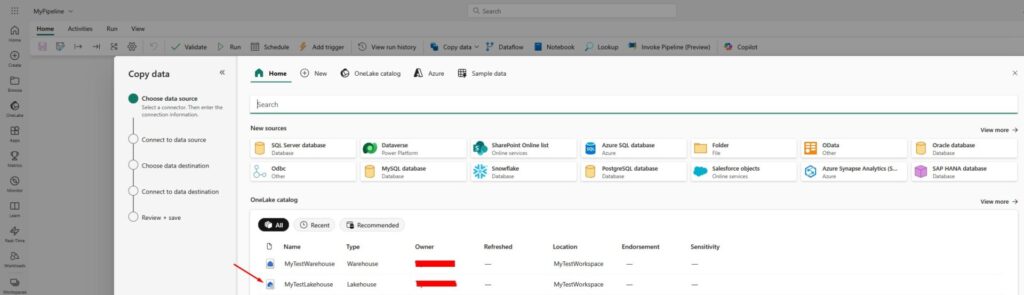
Now we will get to the Connect to data source screen where we will select the tables that we would like to copy:
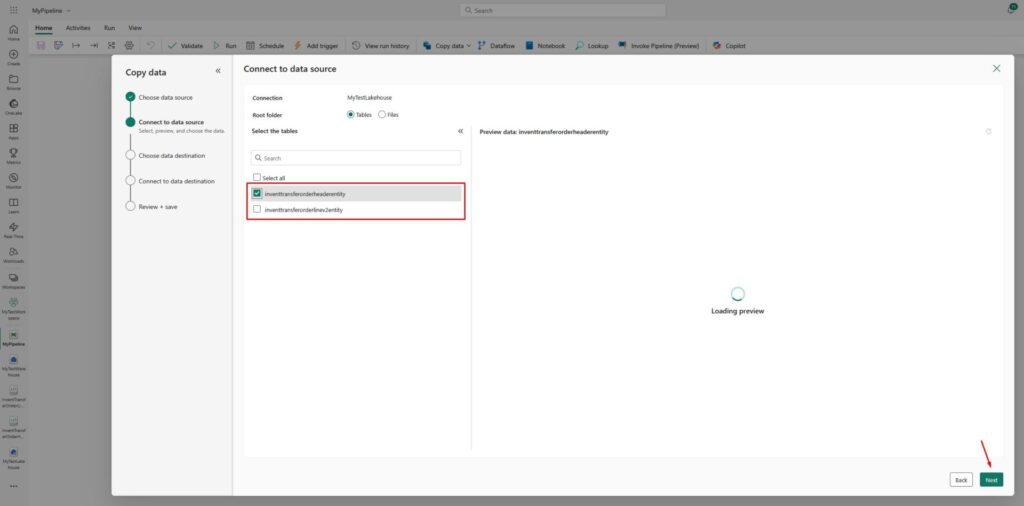
In my example, I have two tables. In your case, you could have much more. Select the tables you want to copy to your data warehouse, and click Next.
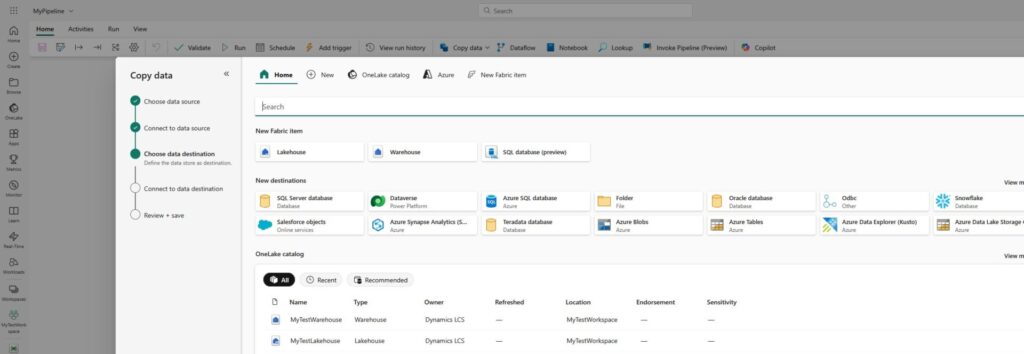
Now, we will select our data warehouse (in my case it’s called MyTestWarehouse) as a destination and click Next:
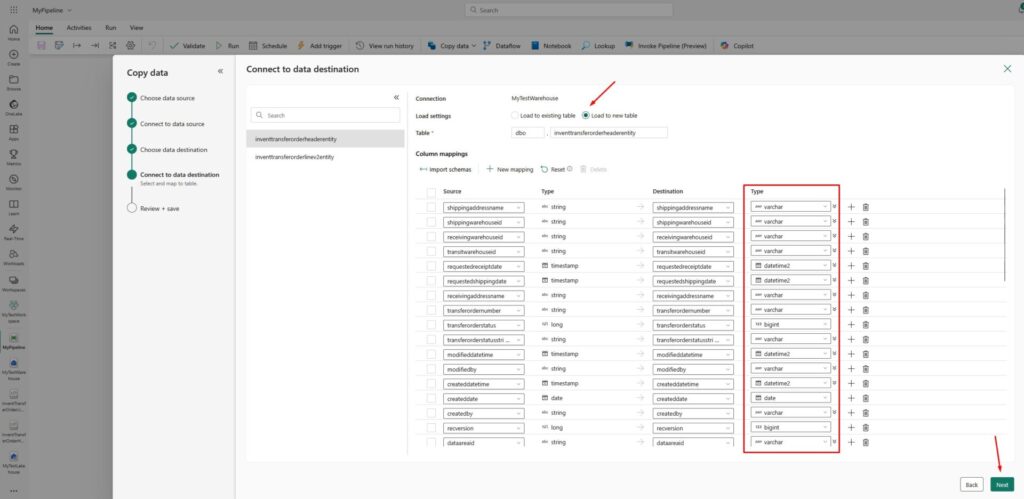
Now, we will connect to our data destination. The system will automatically suggest to load the data to a new table and map the fields from your source (lakehouse) to the new fields in a destination (warehouse). Change the data type if needed and click Next again:
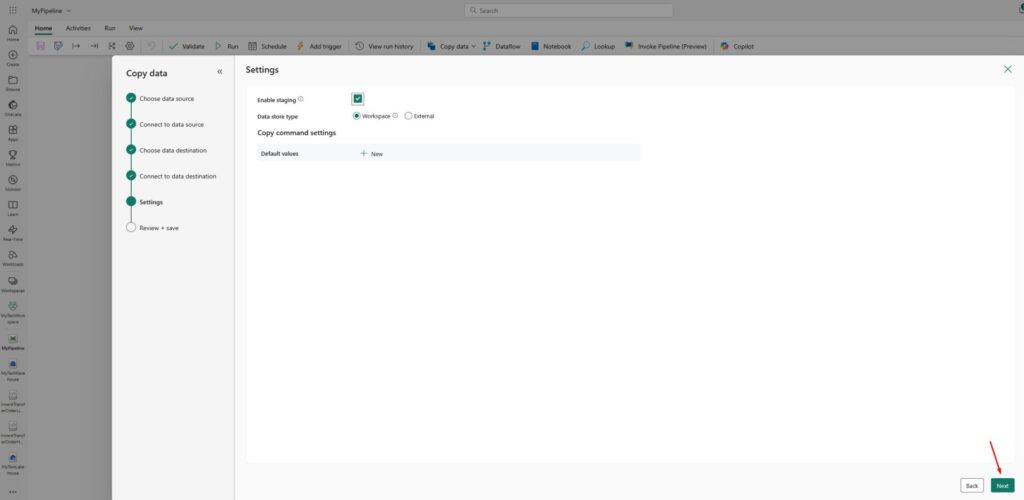
Now, on the Settings screen, leave everything as it is and click Next:
Review and save the copy data job:
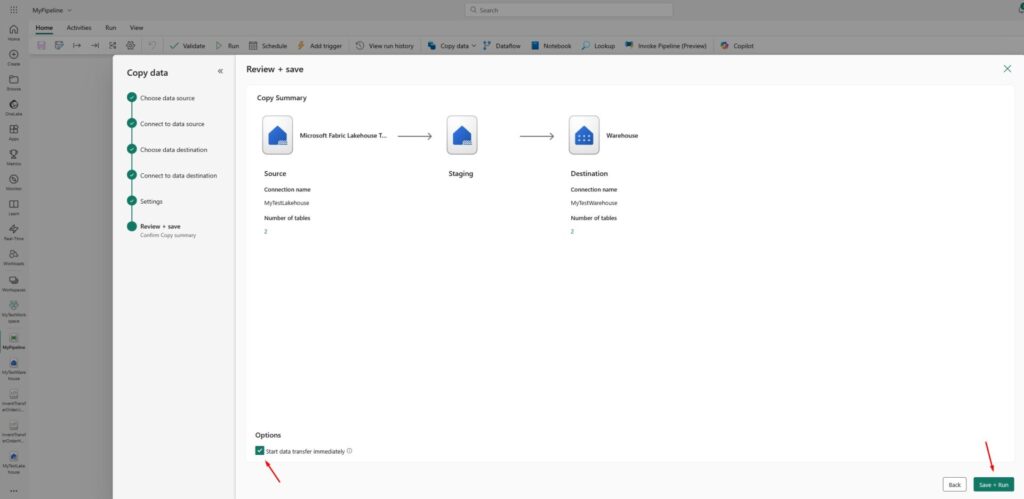
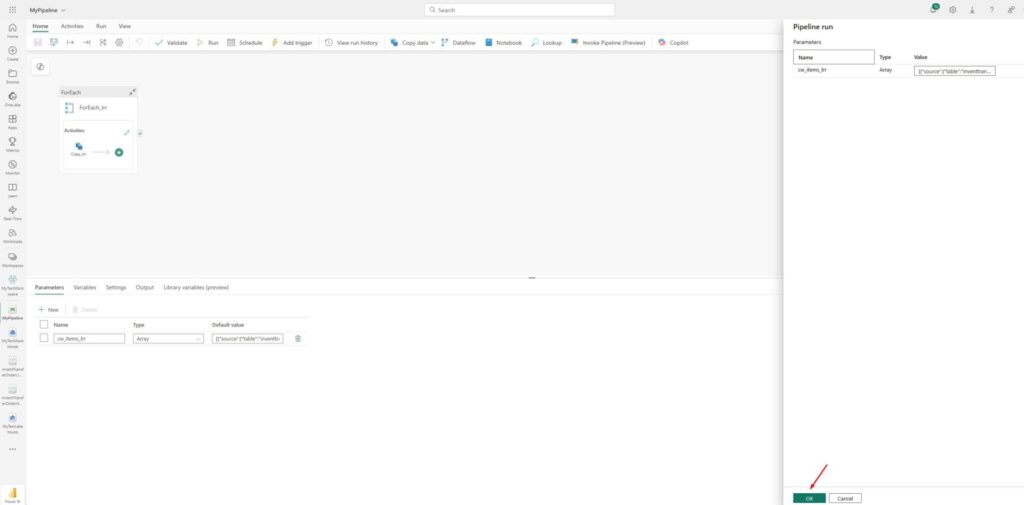
After some time, you will see that the pipeline succeeded:
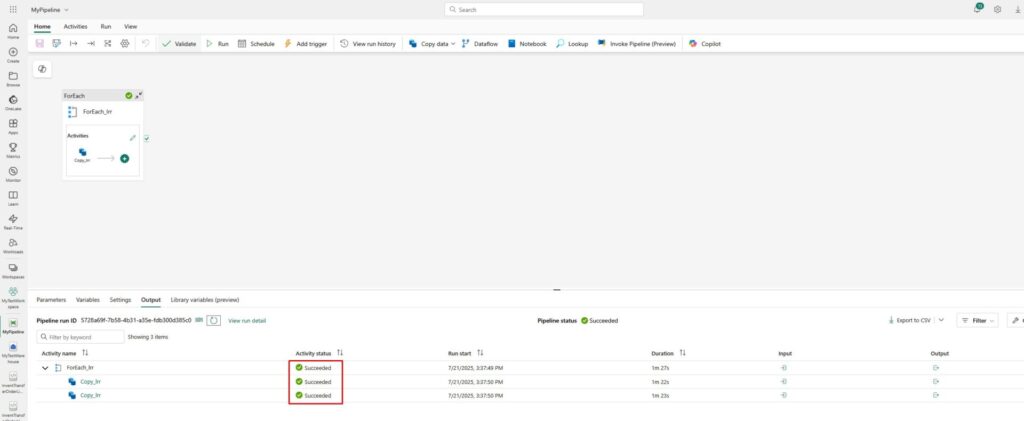
…and if you go back to your warehouse, you will see that both the tables and data are there:
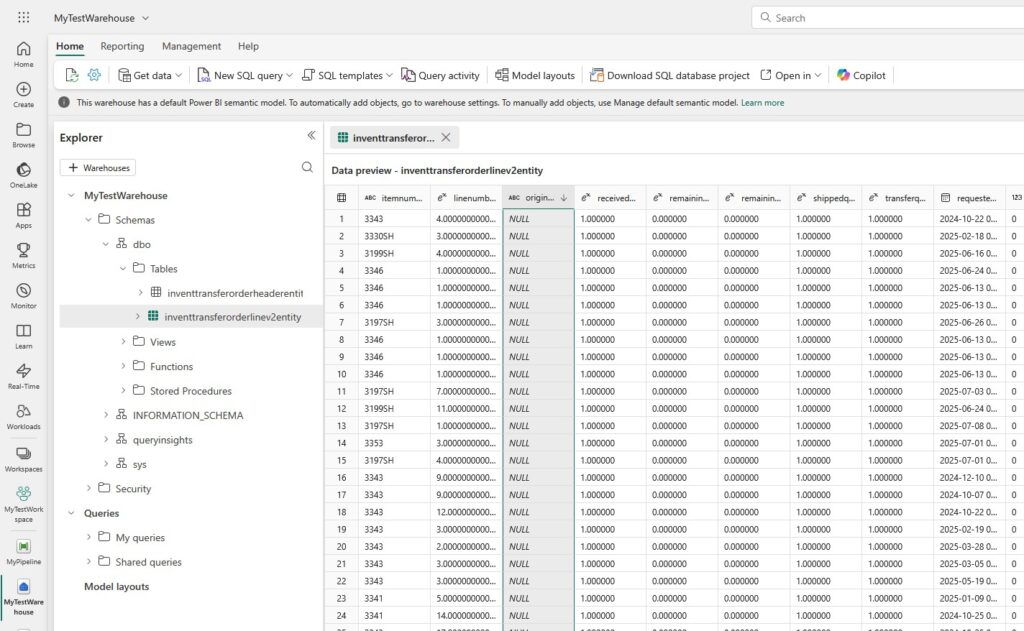
Final Thoughts
So, to wrap it up: Microsoft Fabric Data Warehouse is Microsoft’s modern solution for handling structured data in the cloud. It combines the familiarity of SQL with the power and flexibility of cloud storage. Whether you’re building your first warehouse or migrating from an older system, Fabric makes the process simple and powerful.
Hope this helps! If you’re just getting started with Fabric, feel free to explore more of my blog posts here. Recently, I wrote a blog post on How do I Give Access to Microsoft Fabric, so make sure you check it out.
If you want to learn more about Microsoft Fabric Data Warehouse, make sure you check out this link. There is also a great book on Amazon called Learn Microsoft Fabric: A practical guide to performing data analytics in the era of artificial intelligence that covers some interesting topics.
