In my previous tutorial, we talked about SQL Server views, how they work, how to create them, and why they’re useful for simplifying complex queries. Now it’s time to take the next step and learn about something even more powerful: stored procedures.
What Are Stored Procedures Used For?
A stored procedure is like a pre-written SQL script saved inside your database. Instead of writing the same SQL statements over and over again, you can create a stored procedure once and simply call it whenever you need it.
For example, if you often run a query to show all customers from a specific country, you can store that query as a procedure and execute it in one line.
Stored procedures are mainly used for:
- Reusing SQL code – write once, use multiple times
- Simplifying complex logic – you can combine multiple SQL statements inside one procedure
- Improving performance – SQL Server compiles and optimizes stored procedures, so they can run faster than ad-hoc queries
- Enhancing security – you can grant users permission to run a procedure without giving them direct access to the underlying tables
Difference Between Stored Procedure and View in SQL Server
It’s easy to confuse stored procedures and views since both are reusable objects in SQL Server. However, they’re quite different in how they work.
- A view is basically a virtual table. It’s used to simplify data access by wrapping a SELECT query. You can query a view as if it were a regular table.
- A stored procedure can do more – it can include SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE statements, conditional logic (IF/ELSE), loops, and even call other procedures.
If a view is like a window into your data, a stored procedure is more like a function that can perform actions.
How to Create a Stored Procedure in SQL Server
Let’s look at a simple example using the Northwind database. Suppose we want to create a stored procedure that returns all customers from a specific country.
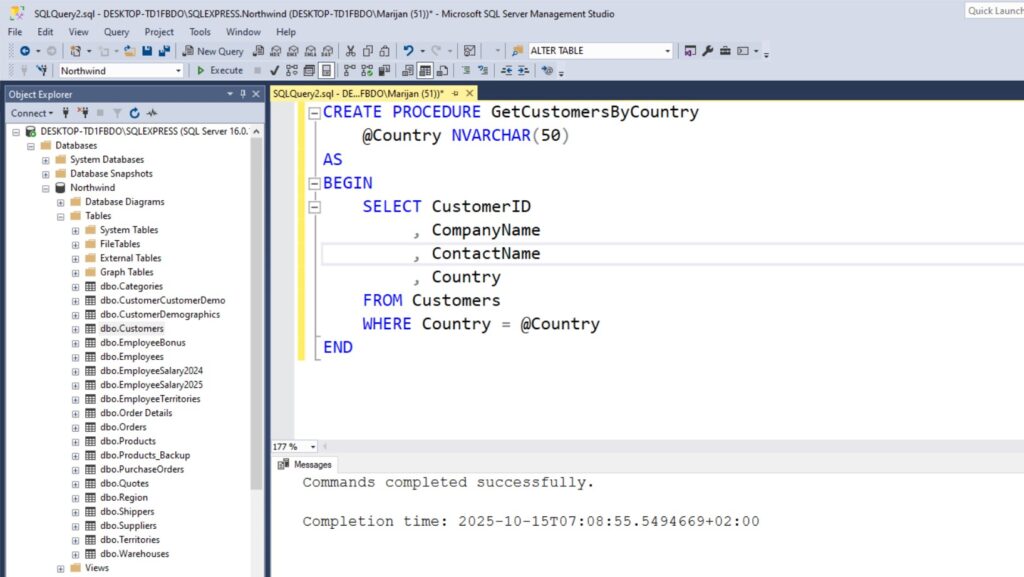
CREATE PROCEDURE GetCustomersByCountry
@Country NVARCHAR(50)
AS
BEGIN
SELECT CustomerID
, CompanyName
, ContactName
, Country
FROM Customers
WHERE Country = @Country
END
Now, to run this procedure, simply execute:
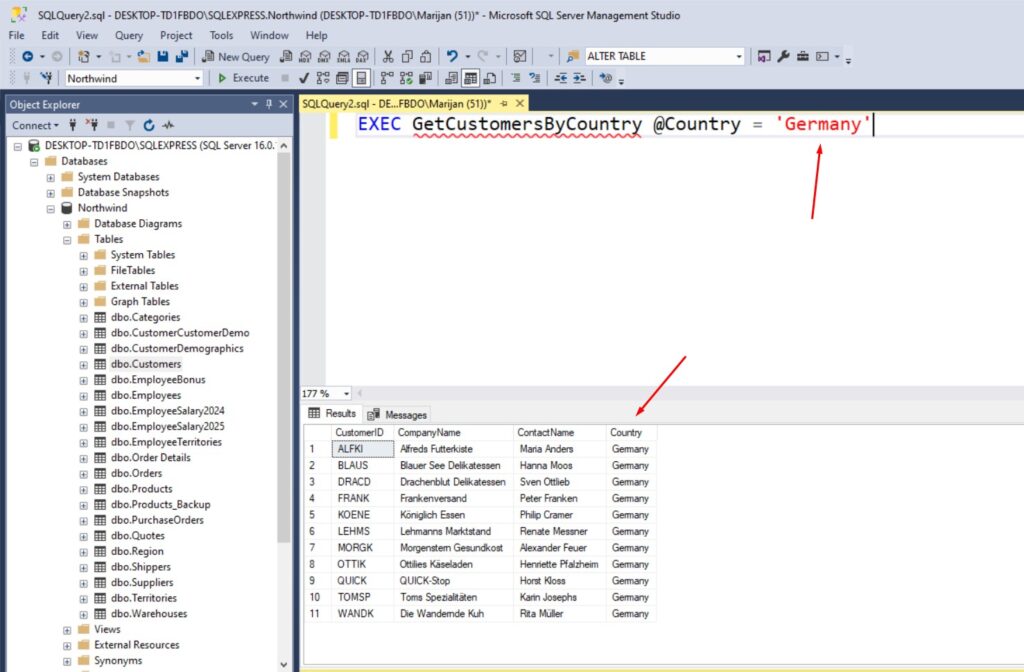
EXEC GetCustomersByCountry @Country = 'Germany'
This will return all customers from Germany:
How it works:
CREATE PROCEDUREdefines a new stored procedure.@Countryis a parameter that you can pass when executing it.- The query inside
BEGINandENDruns when the procedure is called.
How to Update a Stored Procedure in SQL Server
If you want to modify an existing procedure (for example, add more columns), use the ALTER PROCEDURE statement:
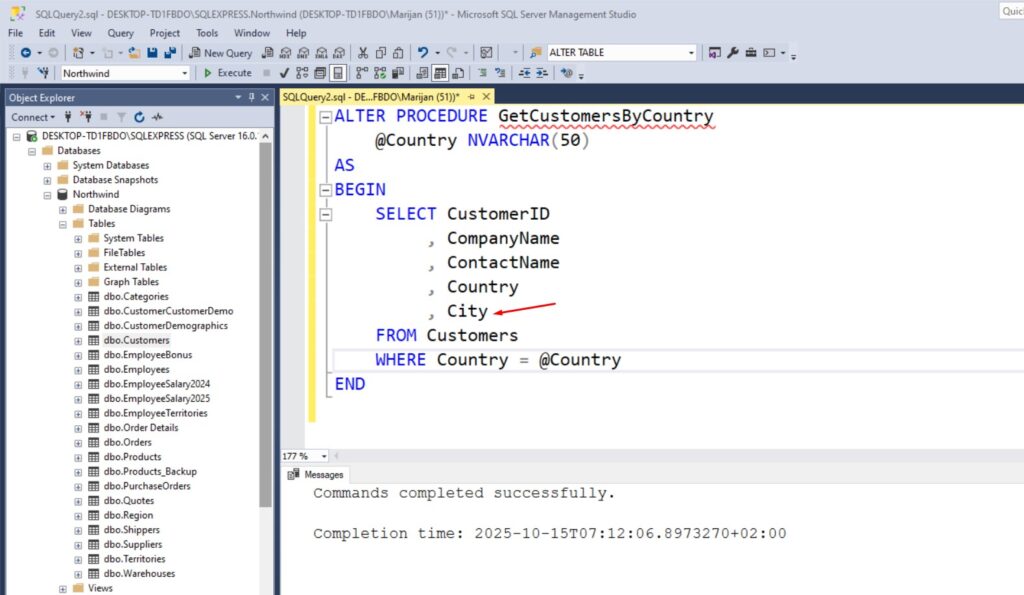
ALTER PROCEDURE GetCustomersByCountry
@Country NVARCHAR(50)
AS
BEGIN
SELECT CustomerID
, CompanyName
, ContactName
, Country
, City
FROM Customers
WHERE Country = @Country
END
Here is what it looks like in SSMS:
How to Delete a Stored Procedure in SQL Server
To remove a stored procedure you no longer need, use:
DROP PROCEDURE GetCustomersByCountry
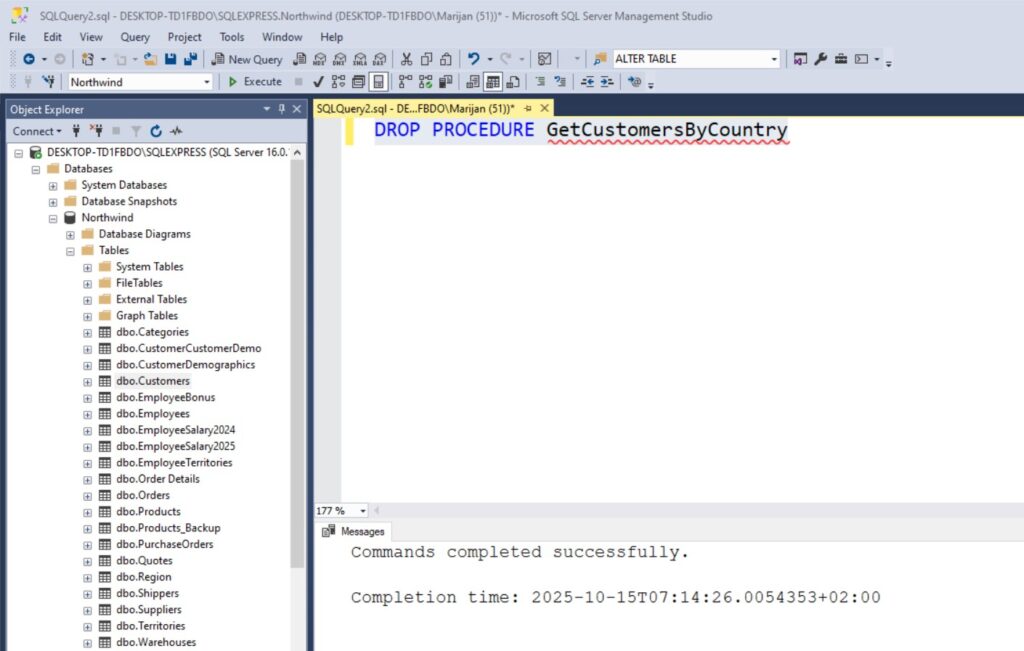
Be careful with this one. Once deleted, it’s gone unless you have a backup or script saved somewhere.
How to View Stored Procedures in SQL Server
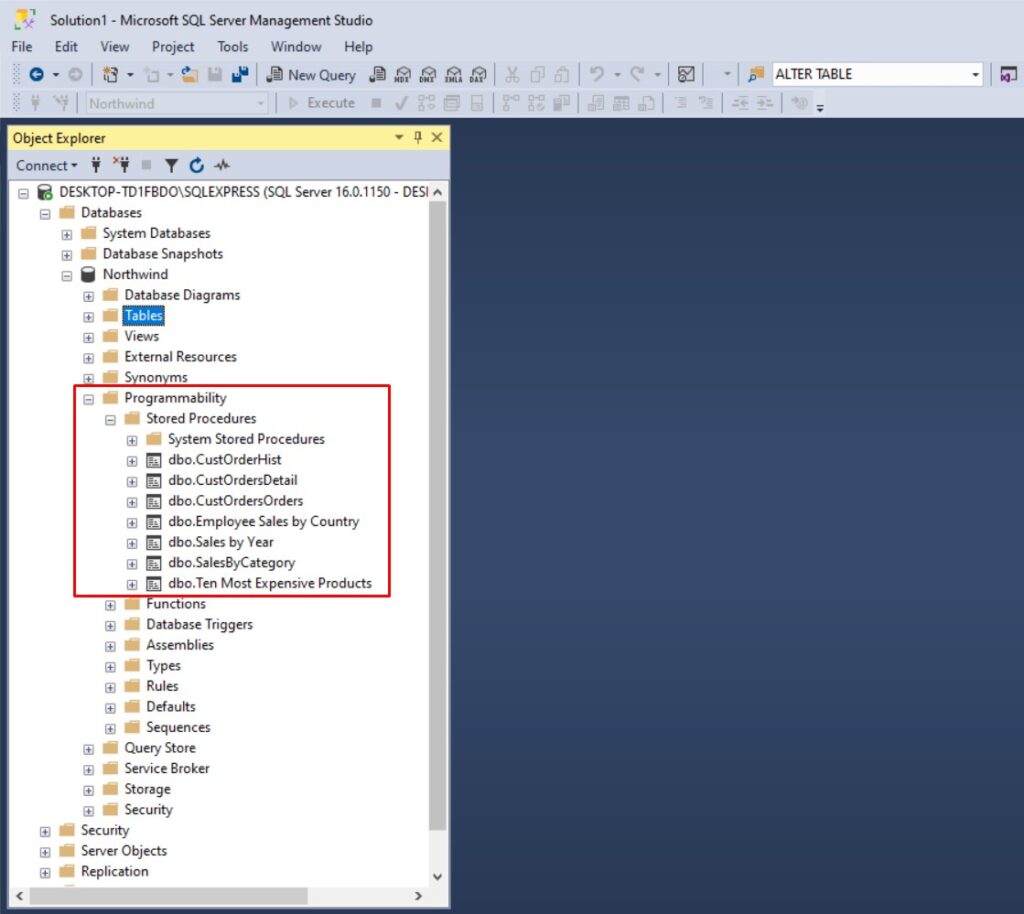
You can easily see all stored procedures in your database using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
Just expand your database and go to Programmability → Stored Procedures:
Or, if you prefer a query:
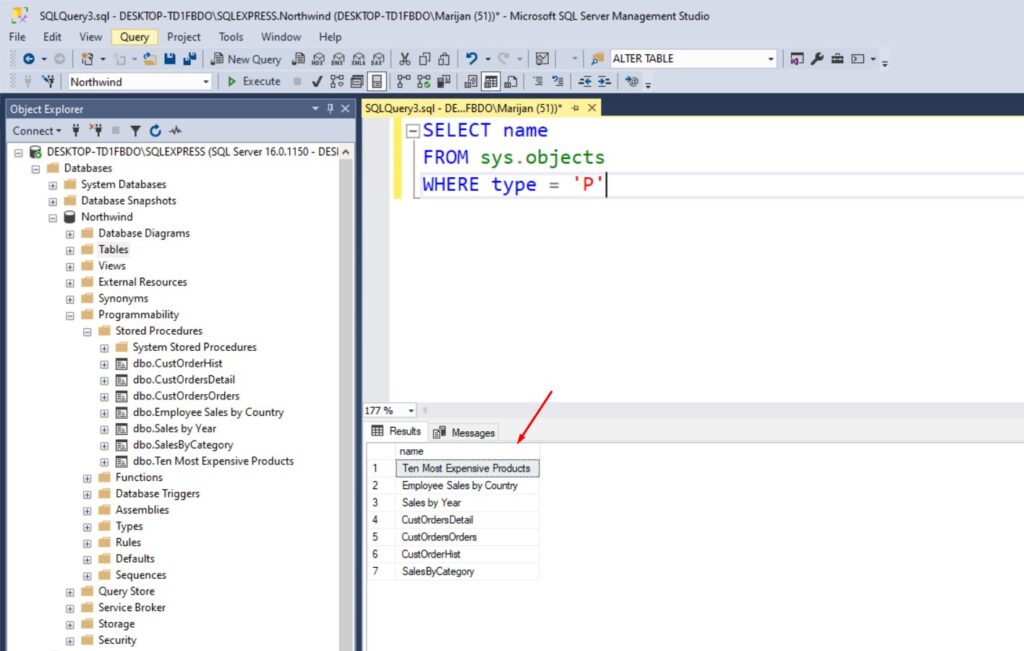
SELECT name
FROM sys.objects
WHERE type = 'P'
This will list all stored procedures in your database:
Is a Stored Procedure Faster Than a Query?
In many cases, yes. Stored procedures are compiled and optimized when first executed, and SQL Server keeps execution plans in memory for reuse. This can make them run faster than executing the same SQL text repeatedly.
However, don’t expect a huge performance boost for very simple queries. The main advantage of stored procedures is organization, security, and reusability rather than pure speed.
Final Thoughts
Stored procedures are one of those SQL Server features that seem complex at first but quickly become essential once you start building larger projects. They help keep your database logic tidy and reusable.
If want to learn more about SQL, check out my last blog post on How to Create Views in SQL Server Management Studio.
If you would like to learn more about programming SQL queries, make sure you buy this book: T-SQL Fundamentals (Developer Reference)
